Air and humidity


Sulfur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen
Fuel gases
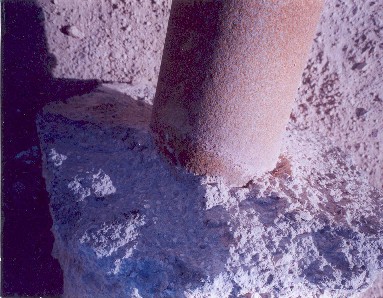
It may, therefore, be observed that corrosion is a potent force which destroys economy, depletes resources and causes costly and untimely failures of plants, equipment and components.
| 1. Introduction to Corrosion | |
|
1.3 Corrosive Environment |
|
|
|